Discover Viking Footprints Across Scandinavia: A Guide to Norse Heritage Landmarks

Updated On: April 24, 2024 by Fatma Mohamed
Scandinavia’s landscape is more than just breathtaking fjords and endless forests; it is a canvas etched with the imprints of Viking ancestors. These impressions offer a rich narrative of seafaring people famed for their explorations, settlements, and influence that extended far beyond their homelands. Our journey through the Norse heritage sites is a step back in time to where myths intertwine with historical feats, revealing the Vikings’ enduring legacy. By visiting these places, we forge a connection with a past civilisation that continues to fascinate and inform our present.
The Vikings’ story is deeply rooted in Scandinavian soil, where they embarked on their daring voyages. Their daily life, maritime prowess, and cultural traditions are vividly captured across key heritage sites in Norway, Sweden, and Denmark. Through museums, archaeological sites, and modern celebrations that echo Viking rituals and customs, we come to understand the intricacies of their world. We learn about their life, from the lands they cultivated and the gods they worshipped to the monuments they left behind. Each site provides a tangible link to understanding the Vikings beyond the common misconceptions, granting us new insights into the complexity of their society.
Table of Contents
The Historical Context of Vikings in Scandinavia

In our exploration, we uncover the significant time frame of the Viking Age and its profound impact on Scandinavia, which went on to influence many regions across Europe. We capture the essence of Viking expansion and how Norse mythology intertwined with the culture of the era.
The Viking Age: A Timeline
The Viking Age lasted from around AD 800 to the 11th century, during which time Scandinavian seafarers made their indelible mark on history. Denmark, Norway, and Sweden were the central powerhouses from which the Vikings embarked on their journeys, shaping the cultural and political landscape of Europe. They established settlements, engaged in trade, and mounted raids, with their influence extending as far as Iceland.
| Century | Event |
|---|---|
| 8th | Beginning of Viking expeditions |
| 9th | Settlements established in Iceland & the British Isles |
| 10th | Christianization of Scandinavia |
| 11th | End of the Viking Age |
Viking Expansion and Influence
Vikings are often depicted as raiders in popular culture, yet their influence stretched further through extensive trade networks and settlements across Scandinavia and other parts of Europe. Their maritime prowess connected them with distant lands, permitting the exchange of ideas, cultures, and goods. The Vikings set foot in England, established the Duchy of Normandy, and even reached the far shores of Iceland and Greenland.
The Intersection of Norse Mythology and Viking Culture
Norse mythology was not just a belief system for the Vikings—it permeated every aspect of their culture. Tales of Odin, Thor, and other deities served as a moral compass and provided context for their explorations and conquests. Artefacts with representations of mythological scenes reflect the deep integration of these beliefs into daily life and how they influenced everything from art to governance.
In understanding these detailed aspects of the Viking Age, we gain a fuller picture of their society and the profound legacy they left in Scandinavia.
Viking Settlements and Daily Life

In exploring Norse heritage, the vestiges of Viking life provide a captivating lens into the past. We delve into the structures where they resided, their societal norms, and the agrarian practices that sustained them.
Exploring the Viking Longhouse
The Viking longhouse was the epicentre of Norse rural living, a multipurpose dwelling that sheltered both people and livestock during the harsh Scandinavian winters. These longhouses, typically constructed from wood, stone, and turf, exemplified Viking craftsmanship and were central to community life. Within these sturdy abodes, families gathered around the hearth, the literal and figurative warmth of Viking daily life.
Viking Social Structure and Lifestyles
Viking society was multifaceted, with a clear social hierarchy that included chieftains, warriors, farmers, and artisans. Daily life in a Viking village exemplified a communal spirit, where roles and responsibilities were shared. In a typical Viking community, men engaged in activities like fishing and trading, while women managed the homestead and bore the critical responsibility of textile production, which was vital to surviving the cold.
Traces of Agriculture and Farmsteads in Scandinavia
Rich archaeological findings illumine the prevalence of Viking farms in the Iron Age. These farmsteads were not just homes, but also the hub of agricultural activities. They practised crop cultivation and animal husbandry. The rural farmstead was a self-sustaining unit, a testament to the Viking’s adeptness in working the land, evidenced by remains of tools and infrastructure used in farming and crafts.
Artifacts and Archaeology
In our quest to trace the Viking footprints across Scandinavia, we encounter an array of fascinating historical remnants preserved through artefacts and archaeological discoveries.
Discovering Treasures from the Viking Past
Unearthing Viking artefacts allows us to piece together snapshots of life during the Viking Age. Amongst the most stirring finds are the Oseberg ship and the burial mounds in Norway, which provide profound insight into Viking burial practices and craftsmanship. The Oseberg ship, found within a sizeable burial mound, stands as a testament to the complexity and artistry of Viking ships, reflecting the importance of maritime prowess in Norse culture.
The Role of Archaeologists in Unearthing History
Archaeologists play a pivotal role in unlocking the silent narratives of the past. Through meticulous excavations of burial grounds in Scandinavia, these historians recover not only Viking tombs but also the day-to-day items that shed light on Norse society. Tools, weaponry, combs, and even bone skates, as found in Coppergate, York, emphasise the Vikings’ intimate relationship with their environment and their resourcefulness.
By cataloguing these artefacts, archaeologists help us understand the scope of Viking civilisation, once dominant across parts of Europe. Our knowledge of Norse history continues to expand with each archaeological endeavour, as the soil of Scandinavia relinquishes its ancient secrets.
Viking Maritime Prowess
Viking maritime prowess is epitomised in their renowned shipbuilding, maritime rituals, and advanced navigation skills which enabled them to traverse treacherous waters and discover new lands.
The Significance of Viking Ships

The Viking ship is a symbol of Norse craftsmanship and seafaring domination. These vessels, including the iconic longships, were not just modes of transportation but embodiments of Viking culture and technological innovation. Among the most famous excavated ships are the Oseberg and Gokstad, exhibited in the Viking Ship Museum in Oslo, which showcase the sophisticated design and beautiful ornamentation typical of Viking nautical engineering. These ships were not only swift but also versatile, capable of traversing open seas and navigating shallow rivers.
Ship Burials and Nautical Legends
Ship burials reflect the intimate relationship Vikings had with the sea. They believed that a boat could carry their elite into the afterlife, encapsulating their status and glory. The act of interring individuals in their boats, surrounded by possessions and even sacrificed animals, has been documented in various archaeological finds. One such site near the Jell Mound divulged a ship’s remnants, placing it closer to the historical shoreline and revealing insights about elite Scandinavian society of the era.
Viking Navigation and Exploration
Our understanding of Norse navigation hints at their advanced knowledge of the seas. Without the compasses that would come later, Vikings used the sun, stars, and possibly even primitive sundials known as sunstones to chart their courses across unfamiliar waters. Their exploration took them from their homelands to far-flung places such as Greenland and Newfoundland, often aboard sturdy knarrs—their cargo ships designed for longer voyages. Their legacy of exploration has marked them as one of history’s great seafaring people, with a love for adventure that has transcended the ages.
Norse Religion and Traditions
Within the rich tapestry of Scandinavian history, Norse religion and traditions stand out as a fascinating cornerstone. Our exploration reveals the complex transformation from paganism to Christianity and the enigmatic myths that define Viking culture.
Pagan Roots and the Conversion to Christianity
Initially, the Nordic populace adhered to a pagan belief system centred on a pantheon of gods and nature worship. Rituals were a part of regular village life, favouring societal survival and prosperity. Christianity’s introduction brought monumental shifts, as leaders like King Olav Tryggvason and St. Olav spurred the religion’s adoption. Their efforts permeated Norwegian society, converting the people from Norse paganism to Roman Catholic Christianity. The remnants of this spiritual transformation are evident in Norway’s landscape, with ancient sacred sites resting alongside medieval churches.
Viking Mythology and the Pantheon of Gods

Viking mythology is a trove of tales and lore central to understanding Norse traditions. The pantheon features prominent deities like Thor, the god of thunder, and Odin, the Allfather of the gods and men. Marvels of mythology were preserved in the sagas, narratives that encapsulate the essence of Viking culture and beliefs. These stories were not mere fantasies but reflections of societal values and natural phenomena. Mythology informed daily life and seasonal rituals, shaping a unique cultural identity that endures in Scandinavian heritage to this day.
Key Viking Heritage Sites in Scandinavia

Scandinavia boasts some of the most significant Viking heritage sites in the world, each offering a unique glimpse into the lives and legacies of the Norse people.
Must-Visit Locations in Norway and Denmark
Norway is home to the Oseberg site featuring a well-preserved Viking ship, revealing insights into Viking maritime skills. Another remarkable site is Avaldsnes, known as Norway’s oldest royal seat. Here, we can walk in the footsteps of Viking kings and uncover Norway’s pivotal role in Norse history. In Denmark, the town of Ribe provides a wealth of Viking age history, with archaeological finds dating back to the 8th century. Jelling is another Danish treasure; it’s dotted with runestones and burial mounds, offering a narrative of Viking culture and artistry.
Sweden’s Rich Viking Legacy
We turn to Sweden to appreciate its Viking legacy, where Birka stands out as one of the earliest urban settlements in Scandinavia. This site includes a museum that hosts a collection of artefacts reflecting the daily life and trade of Vikings. Additionally, the Tune ship, although not as famous as its Norwegian counterparts, is a significant find, providing evidence of Sweden’s shipbuilding prowess in the Viking Age.
Iceland’s Unique Viking History

Iceland presents a unique chapter in Viking history. While it might be more remote, the land of fire and ice has its share of Norse heritage with sites like L’Anse aux Meadows, a UNESCO World Heritage site, which stands as proof of the Viking presence in North America. Back in Scandinavian lands, Gudvangen in Norway is not to be missed; nestled in the Nærøyfjord, it is a living history site where we can immerse ourselves in the Viking experience.
Museums and Education

In Scandinavia, museums play a pivotal role in presenting Viking history, providing immersive educational experiences and conserving precious artefacts for posterity.
Bringing the Past to Life with Interactive Experiences
Our journey through Scandinavia’s Viking heritage is enriched by the innovative displays and educational programmes at various museums. The Lofotr Viking Museum, located in Borg, Norway, recreates a vivid tableau of Viking life through its reconstruction of a Viking chieftain’s house. Visitors can experience hands-on activities, making history both engaging and informative.
In Denmark, specifically in Copenhagen, the National Museum encapsulates the Viking epoch with its extensive collections. Interactive exhibits there allow us to understand the significance of the Vikings in a broader historical context, linking their maritime prowess to the expansion of trade and cultural exchange across Europe.
Conservation of Viking Artifacts for Future Generations
Museums are not just about showcasing history; they are also guardians of our cultural legacy. In Oslo, the enthralling Viking Ship Museum displays three salvaged Viking ships — the Gokstad, Oseberg, and Tune — alongside other archaeological finds, all painstakingly conserved. This preservation work ensures these relics continue to educate and inspire generations to come.
Moreover, in Aarhus and Stockholm, historical museums, including the notable Larvik’s Historical Museum, commit to preserving artefactual integrity. They employ state-of-the-art conservation techniques, underpinning the importance of maintaining these links to our past. Our collective efforts in these cities underscore our dedication to keeping the Viking narrative alive and robust for future learners.
Viking Festivals and Modern Celebrations

We witness a fascinating blend of history and entertainment at Viking festivals, where ancient Norse traditions come alive through vibrant celebrations and interactive experiences.
Annual Events and Their Cultural Significance
Viking festivals are significant cultural events that take a deep dive into Norse heritage. They serve not only as a form of entertainment but also as an educational platform where one can immerse themselves in the lifestyles and milieu of the Viking Age. For instance, the Avaldsnes Viking Festival in Norway is renowned for being the largest such event on the West Coast, offering an authentic experience with over 200 participants from across Europe. The Njardarheimr Viking Village is also a popular destination that recreates a historical Viking settlement, enabling visitors to explore the Viking era in tangible ways.
Significant events like the Gudvangen Viking Market provide an unparalleled opportunity for enthusiasts to celebrate and learn about Viking history and traditions. These gatherings are more than mere spectacles; they are meaningful reconstructions of the past that aim to preserve and honour the legacy of the Vikings.
Participating in Traditional Viking Crafts and Activities
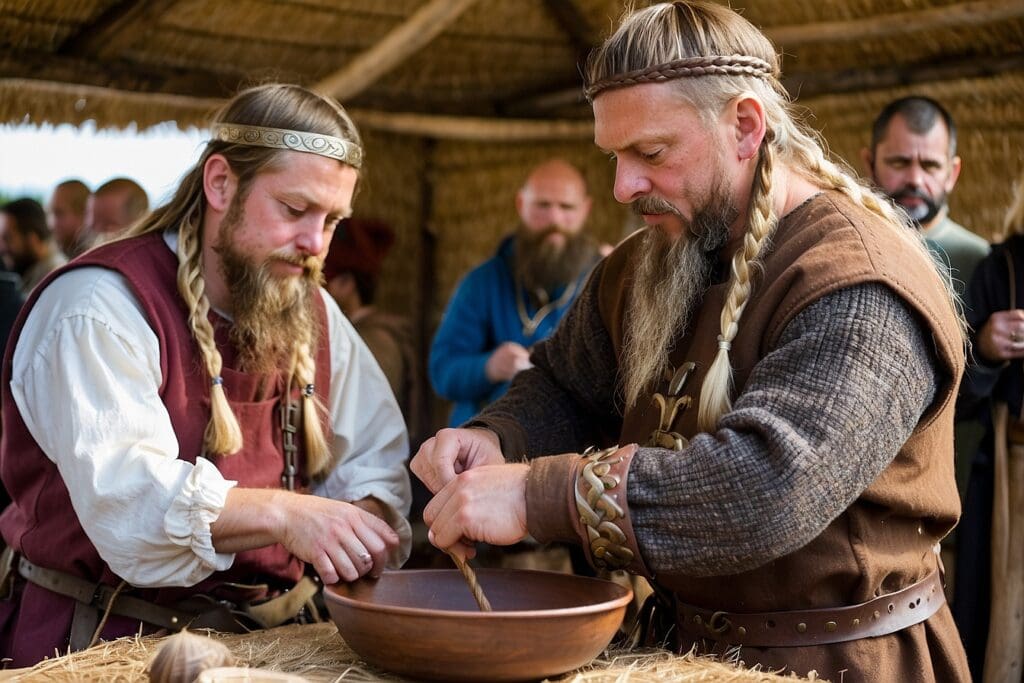

Participation in traditional Viking crafts and activities is central to the festival experience. These gatherings often feature skilled craftsmen demonstrating ancient techniques, such as blacksmithing, weaving, and wood carving. Visitors have the chance to engage directly with these artisans, gaining insights into the meticulous craftsmanship that characterised Norse culture.
At a typical Viking festival, one might encounter a variety of interactive activities, ranging from archery and axe-throwing to educational workshops focusing on Old Norse languages and NorrØna traditions. Musical performances, using period instruments, and storytelling sessions are also commonplace, offering attendees a comprehensive cultural immersion. By engaging in these activities, attendees don’t just observe — they participate in living history, ensuring that the fascinating aspects of Viking life continue to thrive in the modern age.
The Viking Legacy in Place Names and Language

Exploring Scandinavia reveals a tapestry of place names and languages deeply rooted in Viking history. Our investigation uncovers the profound impact of Norse culture on the modern world.
Scandinavian Toponyms with Viking Origins
Toponyms, or place names, are fragments of history etched across landscapes, telling tales of former inhabitants and their languages. Scandinavia is replete with such names that trace back to the Viking Age. Names like Oslo, originally Ánslo, and Stockholm, which combines stock (log) and holm (island), serve as enduring reminders of Norse settlers. More strikingly, areas such as the Shetland and Orkney islands are almost lexicons of the Viking Age, bearing names predominantly of Scandinavian origin. Norwegian influence is unmistakably present in toponyms such as Sumburgh and Scalloway in Shetland, or Orphir and Thorfinn in Orkney, with linguistic roots in Old Norse, a clear testament to the region’s Viking history.
Influence of Old Norse on Contemporary Languages
Old Norse, the language of the Vikings, left a considerable linguistic legacy extending well beyond Scandinavia’s borders. It seeped into the English language, bequeathing a wealth of words that have become commonplace. Terms like sky, egg, and window (from vindauga, or ‘wind eye’) reveal the intimacy of this relationship. Moreover, the impact on dialects across the British Isles, especially in regions with strong Norse connections, underscores how language evolves through cultural intersections. In Scotland’s Orkney and Shetland, traces of this Norse influence permeate the vernacular, a reflection of the islands’ cultural tapestry woven through centuries.
Our journey through Scandinavian toponyms and language illustrates the enduring Viking influence and its role in shaping the culture and identity of modern societies. These place names and words are more than mere labels or terms; they are cultural artefacts, echoing the Norse legacy that continues to resonate today.
Vikings Beyond Scandinavia
As we explore the Viking legacy, it’s paramount to acknowledge their ventures beyond the familiar fjords of Scandinavia. Their footprints stretched across a variety of regions, including the chilly expanse of Greenland and the rugged shores of North America.
Accounts of Norse Explorations in Other Continents
Greenland: Norse explorers, led by Erik the Red, settled on the island around 985 AD, establishing colonies that would endure for centuries. Evidence of these settlements provides us a glimpse into their way of life in these remote regions.
North America: It is widely accepted that the Vikings reached what is now Canada, with the most famous site being L’Anse aux Meadows. Excavations there have revealed the clear marks of Norse presence, asserting their role as some of the first Europeans to set foot on American soil.
Faroe Islands: These islands became a vital waystation during Viking expeditions, acting as a stepping stone across the Atlantic.
England and Russia: The influence of the Vikings extended into England and Russia, with historical accounts detailing their roles in trade, settlement, and societal integration in both regions.
Legacy and Influence in Global Context
Our understanding of the global impact of the Vikings has expanded as we’ve unearthed more about their far-reaching travels and settlements. Here’s how they’ve shaped various aspects of the world:
- Trade Networks: Norse voyagers established extensive trade networks, connecting disparate regions and cultures and thereby influencing global commerce.
- Cultural Exchanges: Interaction with indigenous populations prompted a cross-pollination of ideas, techniques, and genetic heritage, contributing to a richer, more diverse human tapestry.
- The Viking Trail: This network of routes links significant Norse sites across North America, offering us tangible paths to trace their journeys and influence.
Through these examples, it’s clear that the Vikings were not only prolific explorers but also harbingers of change and adaptation – their influence woven into the global historical narrative.
Frequently Asked Questions

In this section, we tackle some of the most common inquiries about Viking footprints across Scandinavia, guiding you to authentic festivals, well-preserved ruins, and the lands that tell the tale of Norse expansion.
What locations host the most authentic Viking festivals in Scandinavia?
In Denmark, the annual Jorvik Viking Festival in York is acclaimed for its historical authenticity and immersive experience. Sweden’s Foteviken Museum hosts an annual Viking market that is also not to be missed for a genuine taste of Norse culture.
Where can I find the most well-preserved Viking ruins in Scandinavia?
Norway’s Lofoten Islands are home to the Borg Viking Museum where you can visit the site of a large Viking Era house. In Denmark, the Viking fortress of Trelleborg near Slagelse is another prime example of preserved Viking architecture.
Which islands in Shetland are known for their Viking heritage?
In Shetland, both Unst and Mainland stand out for their Viking past. Unst, in particular, is often touted to have the highest density of rural Viking sites in the UK, including longhouses and a replica longship.
What are the key historical sites from the Danelaw Viking Age?
Key historical sites from the Danelaw Viking Age include the Jorvik Viking Centre in York, where visitors can explore the Viking-Age city and Coppergate excavation area to learn about the lives of 9th-century Vikings.
Can you visit actual Viking ship remains, and if so, where?
Yes, you can. The Viking Ship Museum in Oslo, Norway, showcases well-preserved Viking ships, including the famous Oseberg and Gokstad ships, alongside a wealth of artefacts from the Viking Age.
What regions did the Vikings originate from within Scandinavia?
The Vikings originally hailed from what are now Norway, Denmark, and Sweden. They were primarily from coastal areas, using their advanced seafaring skills to explore and settle across vast distances.






